rfid passive and active tags Unlike active RFID tags, passive RFID tags only have two main components – the tag's antenna, and the microchip or integrated circuit (IC). As the name implies, passive tags wait for a signal from an RFID reader. ACS ACR122U-SDK NFC Contactless Smart Card Reader Software .
0 · where are active rfid used
1 · rfid tags passive vs active
2 · long range active rfid tags
3 · examples of active rfid tags
4 · do rfid tags need batteries
5 · active rfid tracking system
6 · active rfid tags cost
7 · active rfid tags and readers
Square Reader. Square Invoices. Square Appointments. Customer feedback. .
There are two kinds of RFID systems that exist- passive and active. If you're new to RFID, you might be wondering what the difference is between these types, and which one is best for your application. Below, we provide a short answer to these questions and more along with a more complex, long-form answer. See more
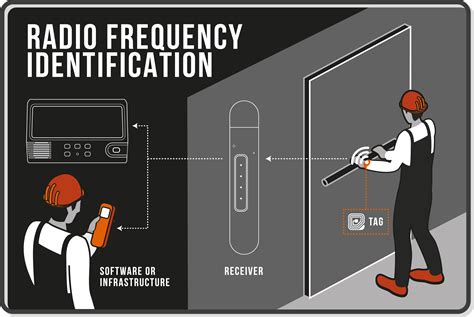
Passive RFID systems use tags with no internal power source and instead are powered by the electromagnetic energy transmitted from an . See more
Key Differences: Active RFID Vs Passive RFID. Range of operation. Battery requirements. Cost. Data storage and transmission capabilities. Reliability and durability. Types of Passive RFID Tags & Labels. Inlays. Paper .
Unlike active RFID tags, passive RFID tags only have two main components – the tag's antenna, and the microchip or integrated circuit (IC). As the name implies, passive tags wait for a signal from an RFID reader.
Key Differences: Active RFID Vs Passive RFID. Range of operation. Battery requirements. Cost. Data storage and transmission capabilities. Reliability and durability. Types of Passive RFID Tags & Labels. Inlays. Paper Face Tags. Hard Tags. High-Temperature Tags. Rugged Tags. Embeddable RFID Tags. Type of Active RFID Tags. Transponders. Beacons.
The two primary types, Passive RFID and Active RFID, differ significantly in their functionalities, capabilities, and best-suited applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the most suitable option for specific use cases. The main difference between active and passive RFID tags is that an active tag has a battery while a passive tag does not. Many commercially used tags are passive, owing to their significantly lower cost, long life and small size. Overview of Active and Passive RFID Tags. Within the realm of RFID technology, two primary tag categories exist: active and passive RFID tags. Each category exhibits distinct characteristics and functionalities that cater to diverse operational requirements. Four key differences exist between active and passive RFID tags: signal range, cost and lifespan, tag size and suitable attachment methods, and real-time monitoring vs. scanner-based activation. Signal range. The first difference is obvious: since an active RFID tag has a battery-powered transmitter, the range is much longer.
RFID technology utilizes radio waves to automatically identify and track various objects. There are two categories of tags: active RFID tags with their own power source, and passive RFID tags powered by the reader’s electromagnetic field.Tag Readability: Passive RFID tags are effective within a range of up to 3 meters, whereas active RFID tags can transmit signals over longer distances, typically up to 100 meters. Energization: Passive RFID tags are energized only when a reader is present, while active RFID tags are always energized and ready to send data. This comprehensive guide delves into passive, active, UHF, HF, and NFC RFID tag types. It explores their applications, considerations for choosing the right tag, and key factors like read range, environmental conditions, and compatibility.
Depending on the power supply method, RFID tags can be divided into two categories: active RFID tags and passive RFID tags. Understanding the working principles, characteristics and application scenarios of these two tags is crucial for enterprises to choose the type of tags that best suits their needs. What are active RFID tags? Unlike active RFID tags, passive RFID tags only have two main components – the tag's antenna, and the microchip or integrated circuit (IC). As the name implies, passive tags wait for a signal from an RFID reader. Key Differences: Active RFID Vs Passive RFID. Range of operation. Battery requirements. Cost. Data storage and transmission capabilities. Reliability and durability. Types of Passive RFID Tags & Labels. Inlays. Paper Face Tags. Hard Tags. High-Temperature Tags. Rugged Tags. Embeddable RFID Tags. Type of Active RFID Tags. Transponders. Beacons. The two primary types, Passive RFID and Active RFID, differ significantly in their functionalities, capabilities, and best-suited applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the most suitable option for specific use cases.
The main difference between active and passive RFID tags is that an active tag has a battery while a passive tag does not. Many commercially used tags are passive, owing to their significantly lower cost, long life and small size.
order a new smart card
Overview of Active and Passive RFID Tags. Within the realm of RFID technology, two primary tag categories exist: active and passive RFID tags. Each category exhibits distinct characteristics and functionalities that cater to diverse operational requirements.
Four key differences exist between active and passive RFID tags: signal range, cost and lifespan, tag size and suitable attachment methods, and real-time monitoring vs. scanner-based activation. Signal range. The first difference is obvious: since an active RFID tag has a battery-powered transmitter, the range is much longer. RFID technology utilizes radio waves to automatically identify and track various objects. There are two categories of tags: active RFID tags with their own power source, and passive RFID tags powered by the reader’s electromagnetic field.
where are active rfid used
Tag Readability: Passive RFID tags are effective within a range of up to 3 meters, whereas active RFID tags can transmit signals over longer distances, typically up to 100 meters. Energization: Passive RFID tags are energized only when a reader is present, while active RFID tags are always energized and ready to send data. This comprehensive guide delves into passive, active, UHF, HF, and NFC RFID tag types. It explores their applications, considerations for choosing the right tag, and key factors like read range, environmental conditions, and compatibility.
rfid tags passive vs active
long range active rfid tags
The NFC Reader Mode is a powerfull way to communicate with NFC tags. For most use cases it is more reliable and more easy to use, compared to the (older) Intent-based way.
rfid passive and active tags|active rfid tags cost