active rfid reader and transmitter Learn which type of active RFID (otherwise known as active RTLS) is right for your specific use case: beaconing RFID, transponding RFID, or intelligent RFID. Grove - NFC Tag is a highly integrated Near Field Communication Tag module,this module is I2C interface,which base on M24LR64E-R,M24LR64E-R have a 64-bit unique identifier and 64 -Kbit EEPROM.Grove - NFC Tag .
0 · where are active rfid used
1 · how to activate rfid tag
2 · examples of active rfid tags
3 · active rfid tracking system
4 · active rfid tracking
5 · active rfid tags and readers
6 · active rfid reader price
7 · active rfid location tracking
uFR XL OEM large-size long-range HF 13.56MHz NFC RFID Reader Writer development kit .RFID long range reader. I need to build 13.56 MHz reader with 20-40 cm reading range.I want to use TRF7963A microcontroller with TRF7960A Evaluation Module.Can you suggest an already built antenna and how to attach it to the .
Learn which type of active RFID (otherwise known as active RTLS) is right for your specific use case: beaconing RFID, transponding RFID, or intelligent RFID. Learn which type of active RFID (otherwise known as active RTLS) is right for your specific use case: beaconing RFID, transponding RFID, or intelligent RFID.
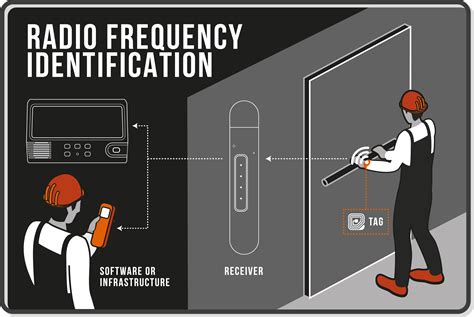
Active RFID systems have three essential parts – a reader or interrogator, antenna, and a tag. Active RFID tags possess their own power source – an internal battery that enables them to have extremely long read ranges as well as large memory banks. Four key differences exist between active and passive RFID tags: signal range, cost and lifespan, tag size and suitable attachment methods, and real-time monitoring vs. scanner-based activation. Signal range. The first difference is obvious: since an active RFID tag has a battery-powered transmitter, the range is much longer.Active RFID tags incorporate a transmitter (transponder or beacon) and a battery as a power source, built together into a single unit. The battery powers the transmitter, enabling it to actively send data to an RFID reader.
The two primary types, Passive RFID and Active RFID, differ significantly in their functionalities, capabilities, and best-suited applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the most suitable option for specific use cases. Active RFID Readers. The reader - or interrogator as it is sometimes called - is the brain of the operation, in that it transmits and receives radio waves to communicate with an active RFID tag.Active RFID tags offer key advantages such as extended reading distances, real-time tracking, and independence from reader power. However, they also present some limitations, including higher costs, limited battery life, and larger size.
Active tags are made up of an integrated circuit, antenna, battery, and an on-board transmitter. The on-board transmitter sends energy directly to the reader rather than reflecting back the energy from the reader (as occurs during coupling).TRANSPONDERS. Transponders are very efficient active tags because they conserve battery life when the tag is out of reach of the reader. When a reader appears within range, it will send a signal and then the transponder will respond with a signal back with the relevant information.Active RFID (radio frequency identification) tags are continuously operating, battery-powered sensors that gather and transmit data to a reading device. An active RFID system consists of a reader, tag and antenna.
Learn which type of active RFID (otherwise known as active RTLS) is right for your specific use case: beaconing RFID, transponding RFID, or intelligent RFID.
where are active rfid used
Active RFID systems have three essential parts – a reader or interrogator, antenna, and a tag. Active RFID tags possess their own power source – an internal battery that enables them to have extremely long read ranges as well as large memory banks. Four key differences exist between active and passive RFID tags: signal range, cost and lifespan, tag size and suitable attachment methods, and real-time monitoring vs. scanner-based activation. Signal range. The first difference is obvious: since an active RFID tag has a battery-powered transmitter, the range is much longer.Active RFID tags incorporate a transmitter (transponder or beacon) and a battery as a power source, built together into a single unit. The battery powers the transmitter, enabling it to actively send data to an RFID reader. The two primary types, Passive RFID and Active RFID, differ significantly in their functionalities, capabilities, and best-suited applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the most suitable option for specific use cases.
Active RFID Readers. The reader - or interrogator as it is sometimes called - is the brain of the operation, in that it transmits and receives radio waves to communicate with an active RFID tag.Active RFID tags offer key advantages such as extended reading distances, real-time tracking, and independence from reader power. However, they also present some limitations, including higher costs, limited battery life, and larger size.
Active tags are made up of an integrated circuit, antenna, battery, and an on-board transmitter. The on-board transmitter sends energy directly to the reader rather than reflecting back the energy from the reader (as occurs during coupling).
TRANSPONDERS. Transponders are very efficient active tags because they conserve battery life when the tag is out of reach of the reader. When a reader appears within range, it will send a signal and then the transponder will respond with a signal back with the relevant information.
how to activate rfid tag
$34.99
active rfid reader and transmitter|examples of active rfid tags