rfid vs chip technology Authors - Chipped Versus Chipless RF Identification: A . - IEEE Xplore To enable NFC Tag Reader functionality on these models, you need to access the Control Center and activate the NFC Tag Reader manually. To add the NFC Tag Reader option in the Control Center, use these steps: 1. .
0 · what is rfid badge
1 · rfid what does it mean
2 · rfid technology explained
3 · rfid is involved when using
4 · rfid explained
5 · rfid acronym meaning
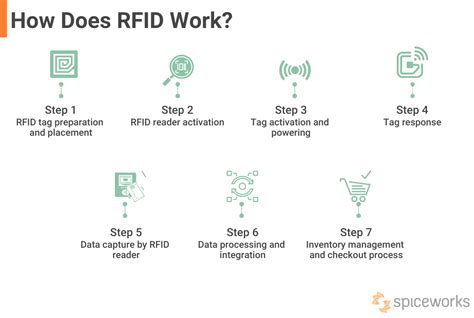
6 · how does a rfid work
7 · how do rfid chips work
281. 282. simple java project to read/write ACR122U . Contribute to smartass33/nfc-card-reader development by creating an account on GitHub.Reading NFC Tags with Android (Kotlin) Near Field Communication (NFC) Tags are used to store Data such as URLs, Contact information or even simple text. Mobile devices that support NFC Technology have the capability .

RF identification (RFID) is a well-known wireless technology that has emerged for capturing data from a stationary or dynamic object. This is one of the key technologies poised to replace barcodes, which are low in data capacity and difficult to reprogram.Sign In - Chipped Versus Chipless RF Identification: A . - IEEE XploreAuthors - Chipped Versus Chipless RF Identification: A . - IEEE Xplore
Figures - Chipped Versus Chipless RF Identification: A . - IEEE XploreCitations - Chipped Versus Chipless RF Identification: A . - IEEE XploreFootnotes - Chipped Versus Chipless RF Identification: A . - IEEE Xplore
This question is for testing whether you are a human visitor and to prevent .This question is for testing whether you are a human visitor and to prevent .
An RFID tag can be affixed to an object and used to track tools, equipment, inventory, assets, people, or other objects. RFID offers advantages over manual systems or use of barcodes. The tag can be read if passed near a reader, even if it is covered by the object or not visible. The tag can be read inside a case, carton, box or other container, and unlike .RF identification (RFID) is a well-known wireless technology that has emerged for capturing data from a stationary or dynamic object. This is one of the key technologies poised to replace barcodes, which are low in data capacity and difficult to reprogram.An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter. When triggered by an electromagnetic interrogation pulse from a nearby RFID reader device, the tag transmits digital data, usually an identifying inventory number, back to the reader.
what is rfid badge
NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in . Anti-shoplifting alarms use a technology called RF (radio-frequency), while a similar (but more advanced) technology called RFID (radio-frequency identification) has many other uses, from tracking pets and public library stocktaking to collecting fares from bus passengers. A small chip -- known as an RFID tag -- is attached to or implanted in an object. The tags contain information that can be read at short range via radio waves. The chip and reader don't have to touch. Some RFID tags can be powered by a .RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.
RFID is more widely applicable across the supply chain, but near-field communication (NFC) has applications in manufacturing settings and can deliver information to retail consumers, among other applications. Other key differences between the technologies include cost and security. Introduction. Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is widely used in industries because it simplifies and automates processes. It uses radio waves to communicate, to identify, and track objects wirelessly, making it a valuable tool for a variety of applications, from supply chain management to access control.
RFID, as a technology that uses radio waves to identify and interact with data, is mainly built from labels, readers and antennas. Among them, the label can be embedded or adhered to the item, and its interior contains an RFID chip and antenna.
RFID and NFC systems use short-range communication to read the ID information on tags. They find use in many spheres of life: contactless payment transactions, asset tracking, real time location systems, access control, retail, marketing, and more.RF identification (RFID) is a well-known wireless technology that has emerged for capturing data from a stationary or dynamic object. This is one of the key technologies poised to replace barcodes, which are low in data capacity and difficult to reprogram.An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter. When triggered by an electromagnetic interrogation pulse from a nearby RFID reader device, the tag transmits digital data, usually an identifying inventory number, back to the reader.
NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in . Anti-shoplifting alarms use a technology called RF (radio-frequency), while a similar (but more advanced) technology called RFID (radio-frequency identification) has many other uses, from tracking pets and public library stocktaking to collecting fares from bus passengers.
A small chip -- known as an RFID tag -- is attached to or implanted in an object. The tags contain information that can be read at short range via radio waves. The chip and reader don't have to touch. Some RFID tags can be powered by a .RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.
rfid what does it mean
RFID is more widely applicable across the supply chain, but near-field communication (NFC) has applications in manufacturing settings and can deliver information to retail consumers, among other applications. Other key differences between the technologies include cost and security. Introduction. Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is widely used in industries because it simplifies and automates processes. It uses radio waves to communicate, to identify, and track objects wirelessly, making it a valuable tool for a variety of applications, from supply chain management to access control.RFID, as a technology that uses radio waves to identify and interact with data, is mainly built from labels, readers and antennas. Among them, the label can be embedded or adhered to the item, and its interior contains an RFID chip and antenna.
what part of the credit card is used for nfc
smartphone nfc card reader
$21.76
rfid vs chip technology|rfid technology explained