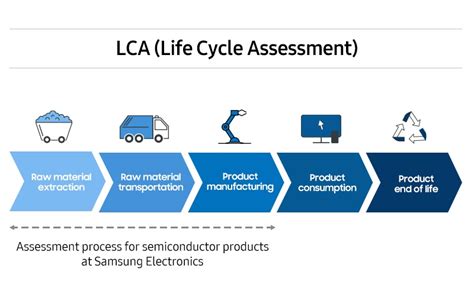
carbon footprint of an rfid chip Vast amounts of energy are required to manufacture the chips that lie beneath the hood of a whole manner of items — from fighter jets and cars, to kettles and doorbells. A team of researchers at.
$389.99Select the department you want to search in .
0 · TSMC, Samsung and Intel have a huge carbon footprint
1 · Figuring Out Semiconductor Manufacturing's Climate
2 · Estimating the carbon footprint of digital agriculture deployment: A
$38.15
Governments and the industry itself are starting to worry what this expansion might mean for chip-making’s carbon footprint and its sustainability generally. Can we make everything in our world smarter without worsening . We presented a methodology to estimate the carbon footprint of digital .
Vast amounts of energy are required to manufacture the chips that lie beneath .
Governments and the industry itself are starting to worry what this expansion might mean for chip-making’s carbon footprint and its sustainability generally. Can we make everything in our world smarter without worsening climate change? I’m here with someone who’s helping figure out the answer. We presented a methodology to estimate the carbon footprint of digital agriculture systems at the scale of a territory, hence better incorporating the diversity of farm sizes and technological system adoptions. Vast amounts of energy are required to manufacture the chips that lie beneath the hood of a whole manner of items — from fighter jets and cars, to kettles and doorbells. A team of researchers at.
Chip makers’ greenhouse gas footprint is expected to widen significantly in the next few years as capacity expands to meet the growth in demand for semiconductors to power energy-efficient devices. Logic and memory chips will be needed in greater amounts, as will discrete, analog, and optoelectronic (DAO) chips.
Wang also stated that most of the energy consumed in the production phase (64 %), principally used to assure high air purity standards into cleanrooms, contributed to the carbon footprint of ICs.
New opportunities to apply RFID are arising notably from the integration of sensor technology to RFID tags. RFID can play an important role in applications helping to deliver a greener world. Even if RFID is not a green technology itself, its applications are helping to lower the carbon footprint in several Abstract. Sensor data can be wirelessly transmitted from simple, battery-less tags using Radio Frequency Identification (RFID). RFID sensor tags consist of an antenna, a radio frequency.
Chip manufacturing is resource intensive and has a significant carbon footprint. It uses large amounts of water, consumes vast amounts of electricity and requires gases that can produce hazardous waste. Sustainability in the chip industry is becoming critical. Semiconductor devices manufactured in 2021 will have a lifetime CO2e footprint of nearly 500 megatonnes (Mt)—15% from materials and equipment (Scope 3 upstream), 20% from device design and manufacturing (Scopes 1 and 2), and 65% from device processing, use, and disposal (Scope 3 downstream). In this Q&A, Berkeley Lab scientists discuss how future microchips could perform better and require less energy than silicon. Governments and the industry itself are starting to worry what this expansion might mean for chip-making’s carbon footprint and its sustainability generally. Can we make everything in our world smarter without worsening climate change? I’m here with someone who’s helping figure out the answer.
TSMC, Samsung and Intel have a huge carbon footprint
We presented a methodology to estimate the carbon footprint of digital agriculture systems at the scale of a territory, hence better incorporating the diversity of farm sizes and technological system adoptions.
Figuring Out Semiconductor Manufacturing's Climate
Vast amounts of energy are required to manufacture the chips that lie beneath the hood of a whole manner of items — from fighter jets and cars, to kettles and doorbells. A team of researchers at. Chip makers’ greenhouse gas footprint is expected to widen significantly in the next few years as capacity expands to meet the growth in demand for semiconductors to power energy-efficient devices. Logic and memory chips will be needed in greater amounts, as will discrete, analog, and optoelectronic (DAO) chips. Wang also stated that most of the energy consumed in the production phase (64 %), principally used to assure high air purity standards into cleanrooms, contributed to the carbon footprint of ICs.New opportunities to apply RFID are arising notably from the integration of sensor technology to RFID tags. RFID can play an important role in applications helping to deliver a greener world. Even if RFID is not a green technology itself, its applications are helping to lower the carbon footprint in several
Abstract. Sensor data can be wirelessly transmitted from simple, battery-less tags using Radio Frequency Identification (RFID). RFID sensor tags consist of an antenna, a radio frequency.
Chip manufacturing is resource intensive and has a significant carbon footprint. It uses large amounts of water, consumes vast amounts of electricity and requires gases that can produce hazardous waste. Sustainability in the chip industry is becoming critical. Semiconductor devices manufactured in 2021 will have a lifetime CO2e footprint of nearly 500 megatonnes (Mt)—15% from materials and equipment (Scope 3 upstream), 20% from device design and manufacturing (Scopes 1 and 2), and 65% from device processing, use, and disposal (Scope 3 downstream).
auburn football radio atlanta
stream auburn football radio
Estimating the carbon footprint of digital agriculture deployment: A
It comes in two variants – ReadPi 125 KHz frequency (Read Only feature) and ReadPi NFC 13.56 MHz frequency with NFC (Read and Write feature). Both the variants work flawlessly in the real time environment. The .
carbon footprint of an rfid chip|Estimating the carbon footprint of digital agriculture deployment: A