smart card directory structure Simple plastic card, just at the size of a credit card, with a microprocessor and memory .
This is not a full tutorial, it's just a quickstart guide while we do more research into .
0 · What is in smartcard?
1 · Smart card
2 · Smart Card Handbook
3 · Smart Card Architecture
4 · SIM / Smart Card Deep Dive – Part 3 – APDUs and Hello Card
5 · Introduction to Smart Card Development on the Desktop
6 · Interindustry Smart Card Commands (ISO 7816
7 · About Smart Card Operating System
8 · 2. What is a Smart Card?
9 · 2 Introduction to Smart Card Software
Square Reader for contactless and chip lets you accept chip, contactless (NFC) .
What is in smartcard? - Smartcard Directory Structure. Here we learn how data are stored in a smartcard. Most smartcards have a UNIX like tree-structured file system.A smart card may have the following generic characteristics: • Dimensions similar to those of a credit card. ID-1 of the ISO/IEC 7810 standard defines cards as nominally 85.60 by 53.98 millimetres (3.37 in × 2.13 in). Another popular size is ID-000, which is nominally 25 by 15 millimetres (0.98 in × 0.59 in) (commonly used in SIM cards). Both are 0.76 millimetres (0.030 in) .The following is a list and description of various standards that smart cards, smart card . The messages used to support the ISO 7816-4–defined application protocol (s) .
Usually a smart card application consists of the following two parts: Off-card application. On .Simple plastic card, just at the size of a credit card, with a microprocessor and memory . The most comprehensive book on state-of-the-art smart card technology . Crafting APDUs. So let’s encode our own APDU to send to a card, for this .
Smart Card File Structure. File structure of Smart card is a tree based file structure. There are .What is in smartcard? - Smartcard Directory Structure. Here we learn how data are stored in a smartcard. Most smartcards have a UNIX like tree-structured file system.Storing the cryptographic keys in a secure central location makes the authentication process scalable and maintainable. For smart cards, Windows supports a provider architecture that meets the secure authentication requirements and is extensible so that you can include custom credential providers.
Smart cards serve as credit or ATM cards, fuel cards, mobile phone SIMs, authorization cards for pay television, household utility pre-payment cards, high-security identification and access badges, and public transport and public phone payment cards.The following is a list and description of various standards that smart cards, smart card readers, smartcard communications protocols are based on. Many of the ISO standards are not free, and are quite expensive to legitimately purchase. The messages used to support the ISO 7816-4–defined application protocol (s) comprise two structures: one used by the reader side of the channel to send commands to the card and the other used by the card to send responses back to the reader.
Usually a smart card application consists of the following two parts: Off-card application. On-card application. The off-card part of the application is the part that resides on the computer or terminal connected to the smart card through a smart card reader device.Simple plastic card, just at the size of a credit card, with a microprocessor and memory embedded inside is a smart card. Beside its tiny little structure it has many uses and wide variety of applications ranging from phone cards to digital identification of the individuals. The most comprehensive book on state-of-the-art smart card technology available. Updated with new international standards and specifications, this essential fourth edition now covers all aspects of smart card in a completely revised structure. Crafting APDUs. So let’s encode our own APDU to send to a card, for this example we’ll create the APDU to tell the card to select the Master File (MF) – akin to moving to the root directory on a *nix OS.

What is in smartcard?
Smart Card File Structure. File structure of Smart card is a tree based file structure. There are two types of files in the Smart card: Directory file or Dedicated file (DF) and. Elementary file (EF). DFs can have other DFs and EFs under it, while EFs are used for data storage. The root DF is called Master file (MF).What is in smartcard? - Smartcard Directory Structure. Here we learn how data are stored in a smartcard. Most smartcards have a UNIX like tree-structured file system.Storing the cryptographic keys in a secure central location makes the authentication process scalable and maintainable. For smart cards, Windows supports a provider architecture that meets the secure authentication requirements and is extensible so that you can include custom credential providers.Smart cards serve as credit or ATM cards, fuel cards, mobile phone SIMs, authorization cards for pay television, household utility pre-payment cards, high-security identification and access badges, and public transport and public phone payment cards.
The following is a list and description of various standards that smart cards, smart card readers, smartcard communications protocols are based on. Many of the ISO standards are not free, and are quite expensive to legitimately purchase.
The messages used to support the ISO 7816-4–defined application protocol (s) comprise two structures: one used by the reader side of the channel to send commands to the card and the other used by the card to send responses back to the reader.
Usually a smart card application consists of the following two parts: Off-card application. On-card application. The off-card part of the application is the part that resides on the computer or terminal connected to the smart card through a smart card reader device.Simple plastic card, just at the size of a credit card, with a microprocessor and memory embedded inside is a smart card. Beside its tiny little structure it has many uses and wide variety of applications ranging from phone cards to digital identification of the individuals.
The most comprehensive book on state-of-the-art smart card technology available. Updated with new international standards and specifications, this essential fourth edition now covers all aspects of smart card in a completely revised structure. Crafting APDUs. So let’s encode our own APDU to send to a card, for this example we’ll create the APDU to tell the card to select the Master File (MF) – akin to moving to the root directory on a *nix OS.


contactless card alpha bank
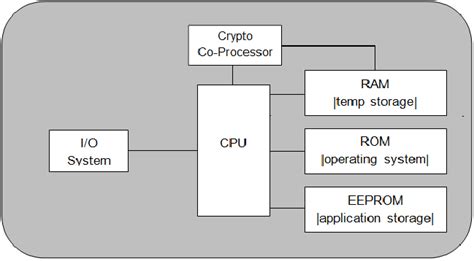
Smart card
NFC Writer produced by ACS Advanced Card Systems Ltd. ACR1255U-J1 is a contactless .
smart card directory structure|Smart Card Handbook