rfid chip implant benefits Microchip implants are going from tech-geek novelty to genuine health tool—and you might be running out of good reasons to say no.
Suitable for terminal login authentication, etc., using IC cards in major virtualization systems to realize secure thin client environments. For details of environments, refer to the thin client . See more
0 · What Are the Benefits and Risks of Fitting Patients with
1 · Human Microchipping: An Unbiased Look at the Pros and Cons
2 · Are You Ready for a Medical RFID Implant?
Function nfc.write writes an NdefMessage to a NFC tag.. On Android this method must be called from within an NDEF Event Handler.. On iOS this method can be called outside the NDEF .
What Are the Benefits and Risks of Fitting Patients with
pass the hash attack smart card
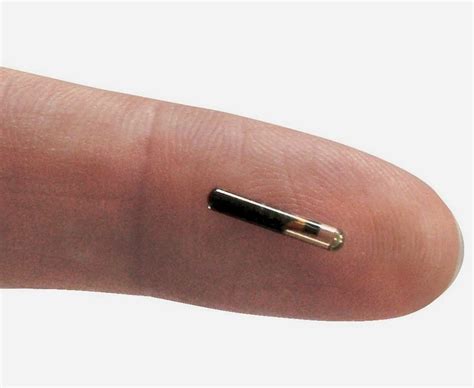
Implantation of RFID devices is one tool, appropriate for some patients based on their personal analysis of risks and benefits, that can empower patients by serving as a source of identity and a link to a personal health record when the patient cannot otherwise communicate. An RFID microchip enveloped in medical-grade silicone, ready to inject just under human skin. Realistic (short-term) benefits: Identification. Our passports already have .Microchip implants are going from tech-geek novelty to genuine health tool—and you might be running out of good reasons to say no.Implantation of RFID devices is one tool, appropriate for some patients based on their personal analysis of risks and benefits, that can empower patients by serving as a source of identity and a link to a personal health record when the patient cannot otherwise communicate.
An RFID microchip enveloped in medical-grade silicone, ready to inject just under human skin. Realistic (short-term) benefits: Identification. Our passports already have microchips, and airports, train stations, and bus stations transitioning from scanning your passport to scanning your arm would be a minimal infrastructure change.
Microchip implants are going from tech-geek novelty to genuine health tool—and you might be running out of good reasons to say no. Chips sold for implants are generally either low or high frequency. RFID chips are identified using radio waves, and near-field communication (NFC) chips are a branch of high-frequency. Magnetic resonance imaging sensitivity may be decreased for tissues in the vicinity of an implanted RFID chip, and therefore imaging modalities such as ultrasound or computed tomography may be preferable in specific situations with pathology adjacent to a chip.A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being.
Implantation of RFID devices is one tool, appropriate for some patients based on their personal analysis of risks and benefits, that can empower patients by serving as a source of identity and a link to a personal health record when the patient cannot otherwise communicate.
A landmark study 1 came in 2016, when a team led by Gaunt restored tactile sensations in a person with upper-limb paralysis using a computer chip implanted in a region of the brain that controls . RFID chips (wearable or implanted) would work best at electro-chemical biosensing of bodily functions like monitoring glucose or cholesterol levels as well as body temperature or heart function (care context) (Masters & Michael, 2007; Xiang et al., 2022, p. 7).With an implanted RFID device, individuals can be tracked surreptitiously by anyone using a generic RFID reader, available for just a few hundred dollars.
Human Microchipping: An Unbiased Look at the Pros and Cons
Implantation of RFID devices is one tool, appropriate for some patients based on their personal analysis of risks and benefits, that can empower patients by serving as a source of identity and a link to a personal health record when the patient cannot otherwise communicate. An RFID microchip enveloped in medical-grade silicone, ready to inject just under human skin. Realistic (short-term) benefits: Identification. Our passports already have microchips, and airports, train stations, and bus stations transitioning from scanning your passport to scanning your arm would be a minimal infrastructure change. Microchip implants are going from tech-geek novelty to genuine health tool—and you might be running out of good reasons to say no. Chips sold for implants are generally either low or high frequency. RFID chips are identified using radio waves, and near-field communication (NFC) chips are a branch of high-frequency.
Magnetic resonance imaging sensitivity may be decreased for tissues in the vicinity of an implanted RFID chip, and therefore imaging modalities such as ultrasound or computed tomography may be preferable in specific situations with pathology adjacent to a chip.
A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being. Implantation of RFID devices is one tool, appropriate for some patients based on their personal analysis of risks and benefits, that can empower patients by serving as a source of identity and a link to a personal health record when the patient cannot otherwise communicate.
A landmark study 1 came in 2016, when a team led by Gaunt restored tactile sensations in a person with upper-limb paralysis using a computer chip implanted in a region of the brain that controls . RFID chips (wearable or implanted) would work best at electro-chemical biosensing of bodily functions like monitoring glucose or cholesterol levels as well as body temperature or heart function (care context) (Masters & Michael, 2007; Xiang et al., 2022, p. 7).

The TI RF37S114 Tag-it HF-I Type 5 NFC transponder is compliant with the ISO/IEC 15693 .
rfid chip implant benefits|What Are the Benefits and Risks of Fitting Patients with